Cosmeceutics
Wojciech Kamysz
Medical University of Gdańsk


According to the Regulation of the European Parliament and Council Regulation (EC) No 1223/2009 a cosmetic product is any substance or mixture intended to be placed in contact with the external parts of the human body (epidermis, hair system, nails, lips and external genital organs) or with the teeth and the mucosa of the oral cavity in order to clean, perfume, change their appearance, protect, keep in good condition or correct body odours. Cosmetics can be rubbed, applied and sprayed on any part of the body, but contained chemical compounds should not interfere with the structure and metabolic processes of the skin.
In contrast to cosmetics, according to the pharmaceutical law, medicine is a substance or mixture of substances intended for preventing or treating disease in human beings or animals, or for the diagnosis, restoring, improving and modifying physiological functions in humans or animals. Drugs can alter the functional state of the body's cells, including skin cells.
Over 25 years ago, an American dermatologist, Albert M. Kligman, defined and introduced the concept of yet another group of products, the so-called cosmeceutics - cosmetics with therapeutic effects; preparations for conditioning and therapeutic activities, which in addition to the care and beautifying features also have the ability to influence physiological processes in the skin and support the treatment of certain dermatoses.
Therefore, cosmeceutics should be inscribed between cosmetics and drugs as they do not belong to any of those groups but they share some of their properties. Comparison of cosmetics, cosmeceutics and drugs is presented in Table 1.
Therefore, cosmeceutics should be inscribed between cosmetics and drugs as they do not belong to any of those groups but they share some of their properties. Comparison of cosmetics, cosmeceutics and drugs is presented in Table 1.
Table 1. Comparison of some characteristics of cosmetics, cosmeceutics and drugs 2.
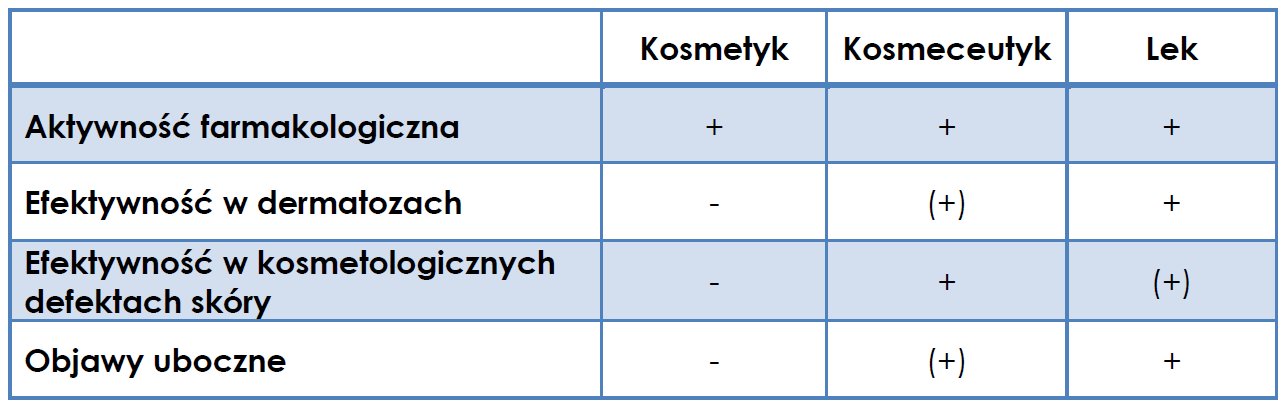
Cosmeceutics act much more stronger than cosmetics, for example they increase the production of new elastic fibers by fibroblasts, reduce wrinkles, eliminate some discoloration, normalize the function of the sebaceous glands or increase the lifespan of skin cells. These care products are stimulating regeneration, improving skin resistance and delay the ageing process. They are particularly important in reducing skin defects such as wrinkles, cellulite, hyperpigmentation, blackheads or striae. They are recommended as supplements to aesthetic medicinal treatments - consolidate and prolong their results. They are also used as a supplement in mesotherapy, laser therapy or peeling. On the one hand, the effectiveness of cosmeceutic is determined by the type of active substance. On the other hand, its concentration is often higher than in cosmetics. Cosmeceutics should not be treated as drugs, but should always be used according to recommendations and for specific ailments.
Main active components of cosmeceutics:
Vitamins – e.g. vitamin A, B, C, E; exhibit effectiveness in the treatment of acne, sun-damages and psoriasis, anti-inflammatory, antibacterial and anti-seborrheic activities. They act as photo-protective and antioxidative agents, can also increase production of collagen, prevent skin ageing, reduce roughness and increase skin flexibility.
Antioxidants – e.g. coenzyme Q10, α-lipoic acid, isoflavones; applied topically, retard aging of the skin, reduce roughness, reduce spots, lines and depth of wrinkles. They can also increase skin resistance to external factors, reduce swelling and erythema, prevent and reduce existing wrinkles caused by UV radiation, strengthen the skin and its elasticity, and increase hydration.
Carboxylic acids (hydroxy-acids) – e.g. mandelic, lactic, malic, citric, tartaric, glycolic acids, cosmeceutics ingredients used to treat acne and acne scars, exfoliate the stratum corneum, unclog sebaceous glands and regulate the secretion of sebum. In addition, they are used for care of mature skin and that damaged by excessive UV - they eliminate pigmentation spots, brighten and bleach discolored patches and stimulate the synthesis of collagen and elastin.
Minerals (metal ions) - e.g. zinc, copper, strontium. The main advantages are protection of the skin and antioxidant activity, facilitating the healing process, the antibacterial, the astringent and anti-dandruff activities. Minerals also minimize the formation of wrinkles and reduce the ageing process of the skin, act as anti-itching and anti-inflammatory agents.
Plant extracts – e.g. horse chestnut extract, arnica, ginkgo biloba, maritime pine bark, green and black tea, witch-hazel and white willow. Exhibit antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities, and improve the appearance of skin. They are also used to smooth out the skin or as the tonicity, normalizing and moisturizing agents.
Peptides – e.g. Pal-KTTKS and argireline. The former is a derivative of a fragment of procollagen type I coupled with palmitic acid. This peptide stimulates the synthesis of collagen and fibronectin. Owing to the presence of fatty acid, the peptide more easily penetrates the stratum corneum of the skin and thus better performs its function which is to reduce wrinkles and minimize the effects of aging. The other one, argirelin, displays similar characteristics as those of the botulinum toxin, by inhibiting the activity of transmembrane proteins of SNARE complex. The purpose to using this peptide is to prevent excessive contractility of fibroblasts, thereby to reduce facial wrinkles. Some peptides can be used as metals carriers, e.g. GHK (glycyl-L-histidyl-L-lysine peptide) which is the carrier for copper.
GHK stabilizes and facilitates the penetration of copper into the cells enabling the execution of its functions.
Growth factors – e.g. TGFβ , EGF, KGF or PDGF. They accelerate wound healing by inducing the synthesis of collagen, elastin, or glycosaminoglycans. They can also exert corresponding effect at the application site as a result of stimulation or inhibiton of cell proliferation and differentiation. They may also mediate angiogenesis. Owing to their specific properties, growth factors accelerate wounds healing and inhibit the skin ageing which is partially due to excessive exposure to UV radiation.
Cosmeceutics represent a group of cosmetic products encompassing a number of compounds with different biochemical activity. Many cosmeceutics could also be used in the treatment of skin discoloration or wrinkles reduction. Numerous studies have shown that some of them accelerate the healing of wounds, including postoperative wounds and also maintain the aesthetic effects of the treatments. Owing to their properties, cosmeceutics can be used successfully as complements to a standard dermatological treatment regimen. However, consumer should retain a reserve and distance to the product and maintain consciousness to do not treat them as a kind of "panacea". Cosmeceutics should be used only after consultation with a dermatologist, pharmacist, or cosmetologist. Ignorance of the substances contained in the preparation and their improper use can have completely opposite effects to those intended and also lead to injury.
Although measurable properties of cosmeceutics have been confirmed in numerous studies, further research must be carried out, due to the fact that cosmeceutics-assisted therapy can bring positive effects not only in the prevention of skin ageing but also in the treatment of dermatological cancers.
References:
-
Rozporządzenie Parlamentu Europejskiego i Rady (WE) nr 1223/2009 z dnia 30 listopada 2009 r. dotyczące produktów kosmetycznych.
-
Kuczyński S.: Kosmeceutyki – więcej niż kosmetyki; „Panacea” 1/2006.
-
Lipiak D.: Kosmeceutyki; „Świat Przemysłu Kosmetycznego” 03/2011.


